Boardline - 022-69318000 / 69301000 | Casualty - 022-69318063 / 64 / +91 86579 07754 | Ambulance - +91 97692 50010 / 75063 58779
Understanding gallstones—symptoms, treatments, and ways to prevent these silent disruptors.
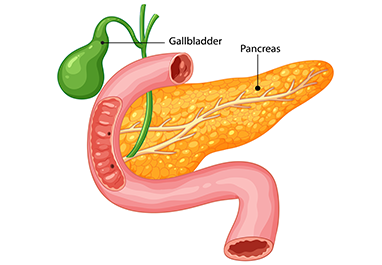
Gallstones are hardened deposits formed within the gallbladder, made up of cholesterol or bilirubin. In adults, abdominal pain is often due to gallstones. It has a varied clinical presentation. Timely diagnosis and treatment help. Bile is a fluid secreted by the liver. It carries chemicals to help digest dietary fat. The gallbladder stores and concentrates the bile. Multiple factors can alter the delicate balance between components of bile, leading to precipitation and gallstone formation. Gallbladder dysmotility, obesity, excess secretion of cholesterol, and bacterial infection increase the risk of gallstone formation. The symptoms: Typically, there is severe pain in the right upper quadrant that comes and goes. It can be severe in intensity. Some individuals don’t have pain but have a feeling of excessive gases, acidity, bloating, burning sensation, etc. If the stone has migrated and has caused complications like jaundice or pancreatitis, there will be yellowish discoloration of the eyes and urine, severe pain radiating to the back, severe itching of the skin, and/or fever.
The diagnosis: Gallstones are readily diagnosed by ultrasound examination of the abdomen. At times, advanced imaging modalities like MRI, and CT scans may also be required. Stages and treatment: Around 5–10% of the population has gallstones. If gallstones are associated with symptoms (symptomatic gallstones), immediate medical attention is mandatory. The standard treatment for symptomatic gallstones is laparoscopic cholecystectomy.
Delay is an invitation to trouble. Medicines have a very minimal role in managing gallstones. Gallbladder surgeries are routinely done by small single skin incision at the navel (Single Incision Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy). It is safe, cosmetic, and leads to a quick recovery. If stones are not associated with symptoms (asymptomatic gallstones), not everyone requires surgery. The attending doctor has to consider multiple factors, like the size of the stones, the age of the patient, the native place of residence, etc., before recommending treatment.
Preventive measures: Increased secretion of cholesterol in the bile and obesity are known risk factors for gallstone formation. Hence, it is postulated that gradual weight loss and well-balanced meals without excess fat may prevent gallstone formation. Gallstones are multifactorial in origin and can lead to mild to severe symptoms. Surgery is often required and can be done with a single-incision laparoscopic approach.
Following these basic principles can help you make the most of the festive season while not compromising your health and skin.
Dr. Hemant Jain, Laparoscopic and GI Cancer Surgeon at Lilavati Hospital